Scheduling Pods 1: Taint and Tolerance
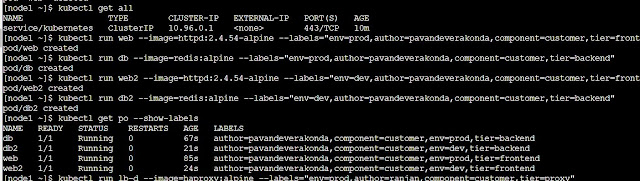
Node in the Kubernetes cluster are schedule the pods as per the Node level Taints will control the Pod creation on the Node. We can update the taints on one or more nodes with single command. The following are instructions from the kubectl label --help A taint consists of a key, value, and effect. As an argument here, it is expressed as key=value:effect. The key must begin with a letter or number, and may contain letters, numbers, hyphens, dots, and underscores, up to 253 characters. Optionally, the key can begin with a DNS subdomain prefix and a single '/', like example.com/my-app. The value is optional. If given, it must begin with a letter or number, and may contain letters, numbers, hyphens, dots, and underscores, up to 63 characters. The effect must be NoSchedule, PreferNoSchedule or NoExecute. Currently taint can only apply to node. How does Taint - Tolerance works in Kubernetes? Taints allow a node to repel a set of pods. Tolerati...