Understanding Docker Volumes in-depth with real-time scenarios. Where the MongoDB is the backend tier Database and frontend web application using - Mongo-Express container.
Use Case 1: MongoDB container without volume observe what happens to the data.
Use Case 2: After attaching volume = persistence - confirm re-create containers data persist
Use Case 3: Database containerversion changes does not impacts the Data persisted
Let's start the experiment on data persistance.
 |
| Docker Volume deep dive - MongoDB persistant |
To share the sensitive data we use network isolation, which is already discussed in Docker Networks post.
# Create Network docker network create mynetNow let's use this mynet throughout all our use-case examples. MongoDB Connect to Mongo-express which is a member in the same network so that it can access the database
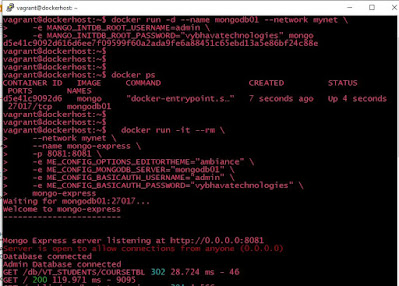
Use Case 1: MongoDB Without any volume - Non Persistence
MongoDB Container without any persistance storage :
docker run -d --name mongodb01 --network mynet \
-e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=admin \
-e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD="vybhavatechnologies" mongo
Aa we have not mentioned any tag after mongo so it will pull the latest mongo image from the docker hub. Validate mongodb container
docker ps -a
If you don't see running docker container for mongodb check the logs using
docker logs mangodb -fhere -f is optional to see the floating log content. If all good, we can run the next container Mongo-express
# Web client - based on nodejs express fraework package
docker run -it --rm \
--network mynet \
--name mongo-express \
-p 8081:8081 \
-e ME_CONFIG_OPTIONS_EDITORTHEME="ambiance" \
-e ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_SERVER="mongodb01" \
-e ME_CONFIG_BASICAUTH_USERNAME="admin" \
-e ME_CONFIG_BASICAUTH_PASSWORD="vybhavatechnologies" \
mongo-express
This container is for the use-and-throw container so used --rm in the above command.
On the browser open the mongoexpress web application for example as : http://192.168.33.250:8081/ Enter the user: admin and password as vybhavatechnologies
 |
| Build Stateful application with MongoDB container |
 |
| Collection adding document on mongo-express |
Use Case 2: Docker Volume attached to mongo container
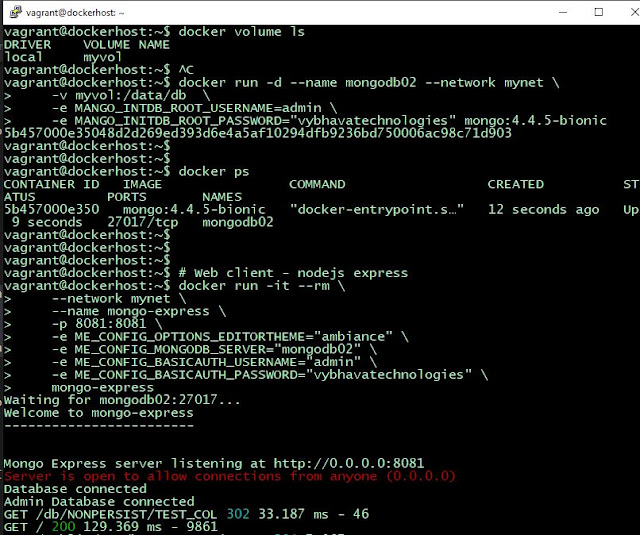
docker volume create myvol docker volume lsNow let's use the volume which is created as named volume on the Docker host machine. Attach it to the MongoDB container.
docker run -d --name mongodb02 --network mynet \
-v myvol:/data/db \
-e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=admin \
-e MANGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD="vybhavatechnologies" mongo:4.4.5-bionic
This time image tag I'm using mongo:4.4.5-bionic, I've tried windows server but it didn't work!
# Check the contianer up
docker ps
# Web client - nodejs express
docker run -it --rm \
--network mynet \
--name mongo-express \
-p 8081:8081 \
-e ME_CONFIG_OPTIONS_EDITORTHEME="ambiance" \
-e ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_SERVER="mongodb02" \
-e ME_CONFIG_BASICAUTH_USERNAME="admin" \
-e ME_CONFIG_BASICAUTH_PASSWORD="vybhavatechnologies" \
mongo-express
Now let's add documents for each student data[
{ "name": "Vignesh", "Course": "Automations"},
{ "name": "Srinivas", "Course": "AWS Solutions"},
{ "name": "Abhijoy", "Course": "WebLogic"},
{ "name": "Shammi", "Course": "Continerized Solutions"},
{ "name": "Rajsekhar", "Course": "Microsoft Azure DevOps"},
{ "name": "Srikant", "Course": "DB Solutions"},
{ "name": "Viswasri", "Course": "AWS DevOps Solutions"},
{ "name": "Melvin", "Course": "DevOps Solutions"}
]
Now run the removal of containers, add the following alias to .bashrc your docker host machine.
alias dc='docker rm -v -f $(docker ps -aq)' dc docker ps -a # confirm all containers removedNow run the same steps to create the mongodb02 and mongoexpress containers check the data exists and now try to add new document:
{
_id: ObjectId(),
"name": 'Pranavsai',
"Course": 'Analytics'
}
 |
| MongoDB with Volume |
Use Case 3: Database container version changes do not impact Data persistence
docker run -d --name mongodb03 --network mynet \
-v myvol:/data/db \
-e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=admin \
-e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD="vybhavatechnologies" mongo:4
 |
| Docker Hub mongo DB image tags |