Docker Service Stack deployment
To work with Docker service stack deployment we should have an orchestrator either Swarm or Kubernetes. Here, in this post, I will be experimenting with the Docker swarm cluster.
Docker installed machine
Docker swarm initialized and active


It will clearly show how High-Availability can be achieved with the Docker Swarm orchestrator.
Jai Hind!!
Prerequisites
Create the manifestation file that describes the task, which will be available in the service definition. We can use the declarative definitions for each service in a YAML file.
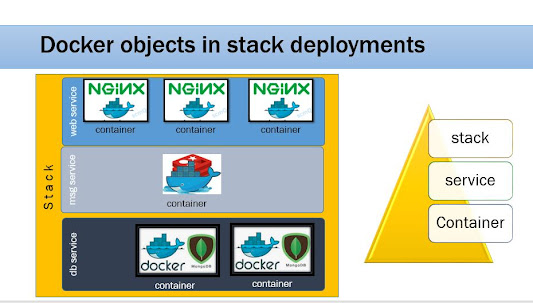 |
| Docker Swarm Service Stack Deployment |
I read the book: Learn Docker - Fundamentals of Docker 19.x, where I found the nice explanation given in the

Let's run the docker swarm visualizer container, which will show the Swarm cluster node status, container service status it will be very clear to understand how the orchestrator capabilities work for Docker containers.
docker run -it –d \ -p 8080:8080 \ -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \ dockersamples/visualizerAlternatively, you can use the docker-compose file as a replacement for the container run command:
version '3'
services:
viz:
image: dockersamples/visualizer
volumes:
- "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"
ports:
- "8080:8080"
You can enhance it's usability with your own parameters to run the containers.When no deployments swarm nodes contain empty:
 |
| Initial Swarm Visualization |
Visualizer shows us the number of master and worker swarm nodes participating in the cluster. The green glow-filled circle indicates the active Node of the Docker Swarm cluster.
Docker stack service deployment
The docker swarm service logs can be viewed in two ways using the parameter as service ID or using service NAME
Run the following docker Stack deployment command as:
Now let's see the deployment of whoami sample:
version: "3.7"
services:
whoami:
image: training/whoami:latest
networks:
- test-net
ports:
- 81:8000
deploy:
replicas: 6
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
labels:
app: sample-app
environment: prod-south
networks:
test-net:
driver: overlay
The menifestation tells about the desired state of the application, where we mentioned what is the port we want to use on the host and corresponding container port. Here 81 is host port, 8000 is container port. This service uses test-net network resource. The deploy section mentioned as replicas: 6, that means 6 containers will be created on Docker Swarm clsuter. You wish to run the multiple containers run parallel on the same node. We can use labels to identify and remove the services in runtime that will help in monitoring the applicaiton, It is also useful to terminate the services by descovering with these labels.
docker stack deploy whoami --compose-file docker-service-whoami.yml
docker stack lsStack deployment automatically creates overlay network
docker network ls docker service ls docker container ls curl http://192.168.33.250:81
The execution will produce output as follows:
 |
| Curl command output from the Docker swarm cluster |
docker service logs whoami_whoami docker service logs kiw9ckp68hu5After the deployment of 'whoami' service see that is distributed amont multiple machines which built-in capability of the Docker swarm.
 |
| Docker Swarm Visualization shows replicas=6 on multi-host deployment |
Docker Cluster Resilience Test case
Here we can do the test for the resilience two levels:- container level
- node level
Use case 1: Container level fail-over
Step 1: Determine the running containers list
Step 2: Remove a container from the stack
Step 3: The service deployment will automatically create the new container to maintain the DESIRED state as 6 when a container removed ACTUAL State gone to 5, to maintain it Docker Swarm will work to birng up the service.
docker container ls docker container rm -f whoami_whoami.3.selectyourown-container docker ps
 |
| Use case 1: Remove a container Swarm service recreate the replacement container |
This concludes containers high availability using service deployment using stack on swarm cluster. The actual real usecase that node level will give HA in tne next.
Use case 2: When the node fails - Service Migration
Brought down the Machine and see the outcome on the Swarm Visualizer:
One your Vagrant machines you can stop one of the node to see the impact how it will recover or maintaine the DESIRED State of replicas=6, Here in our example, the service which is running on node1 continue running on available nodes (mstr, node2) by migrating the service to them. This migration will be taken care by the Docker Swarm automatically. We can also define choices in the YAML file.
 |
| Swarm Visualization of migration of services to other worker: Vagrant node1 halt |
The Visualization tool shows clear picture of how the Docker Swarm capable of migrate the service when there is issue/failure on node.
It will clearly show how High-Availability can be achieved with the Docker Swarm orchestrator.
Jai Hind!!



Comments