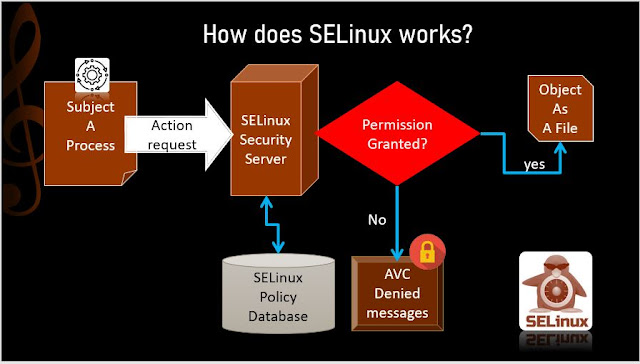
Understanding SELinux How it works
SELinux on Ubuntu
Here is a simple objective of this post is to install, activate and disable the SELinux on Ubunutu.What is actually SELinux?
Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) is a security architecture for Linux® systems that allows administrators to have more control over who can access the system. Security-Enhanced Linux is a Linux kernel security module that provides a mechanism for supporting access control security policies, including mandatory access controls. SELinux is a set of kernel modifications and user-space tools that have been added to various Linux distributions.Here I'll explore the possible options on Ubuntu.
How to install SELinux on Ubuntu?
This regular package installationapt install policycoreutils selinux-utils selinux-basics -y
How to activate SELinux on Ubuntu?
To activate the SELinux we need to edit the config file.selinux-activate
To get this effected need to reboot the Linux VM/machine.
Understanding Configure SELinux
SELinux configuration file available at /etc/selinux/config
The configuration contains two directives in the config file:
I. SELINUX that dictates SELinux Mode and it can have three values as shown
SELinux modules can take one of these three values
1. enforcing - any unauthorized access attempts by users and processes are denied
2. permissive - semi-enabled state, SELinux doesn't apply its policy in Permissive mode, so no access is denied instead it gives a warning
3. disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded
II. SELINUXTYPE tells that what policy will be used.
SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these three values:
default - equivalent to the old strict and targeted policies
mls - Multi-Level Security (for military and educational use)
src - Custom policy built from source
How to disable SELinux on Ubuntu?
To disable this feature edit the config file and changeSELINUX=permissiveto
SELINUX=disable
 |
| after disabled |
How do you know the current mode of SELinux?
There are two options to know about the SELinux current status which includes a current mode.getenforce # to check the current SELinux mode sestatus # SELinux statusExample output of 'sestatus' command
 |
| before reboot sestatus output |
Troubleshooting on SELinux Configuration
Here is a very minute mistake instead 'disabled' used 'disable' then the sestatus shows the 'error' :




Comments
DevOps Training in Bangalore | Certification | Online Training Course institute | DevOps Training in Hyderabad | Certification | Online Training Course institute | DevOps Training in Coimbatore | Certification | Online Training Course institute | DevOps Online Training | Certification | Devops Training Online
This article is very much helpful and i hope this will be an useful information for the needed one.Keep on updating these kinds of informative things. Thank you for sharing wonderful information with us to get some idea about that content.
oracle training in chennai
oracle training institute in chennai
oracle training in bangalore
oracle training in hyderabad
oracle training
oracle online training
hadoop training in chennai
hadoop training in bangalore